
- #Running a stored procedure in sqlpro studio update
- #Running a stored procedure in sqlpro studio series
If you use read uncommitted, changes to data in published tables are replicated as a series of DML statements.
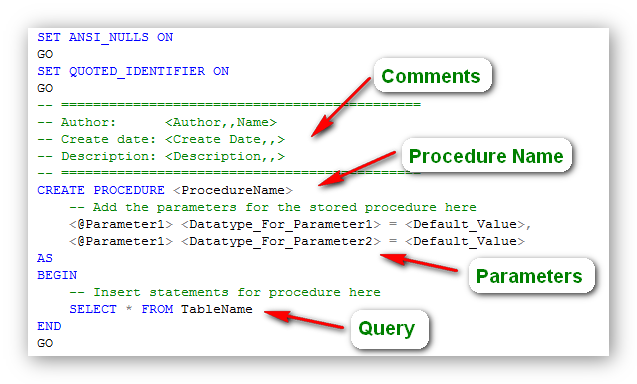
To address these issues, it is required that Subscribers are read-only and that you use an isolation level greater than read uncommitted. Furthermore, because changes made to data by the stored procedure can occur within multiple transactions, data at the Subscribers might not be consistent with data at the Publisher. With the procedure execution option, it is possible that execution could be replicated to all Subscribers regardless of whether individual statements in the stored procedure were successful. This is especially useful for batch operations, such as large cleanup operations. This behavior contributes to making data at the Subscriber consistent with data at the Publisher. If the stored procedure is executed from outside a serializable transaction, changes to data in published tables are replicated as a series of DML statements. The serializable option is recommended because it replicates the procedure execution only if the procedure is executed within the context of a serializable transaction. There are two different ways in which the execution of a stored procedure can be published: serializable procedure execution article and procedure execution article. Types of Stored Procedure Execution Articles For information about schema changes, see Make Schema Changes on Publication Databases. To prevent this, disable the propagation of schema changes before executing ALTER PROCEDURE.
#Running a stored procedure in sqlpro studio update
At the Subscriber, you can modify sp_big_delete to delete only the 1 million rows and not perform the subsequent update to big_table2.īy default, any changes made using ALTER PROCEDURE at the Publisher are propagated to the Subscriber. To reduce the demand on network resources, you should propagate the 1 million row delete as a stored procedure by publishing sp_big_delete. For example, consider sp_big_delete, a stored procedure at the Publisher that has two functions: it deletes 1,000,000 rows from the replicated table big_table1 and updates the nonreplicated table big_table2. This is useful if you want different logic to be executed at the Publisher and Subscriber. However, you can also modify the stored procedure at the Subscriber. Modifying the Procedure at the Subscriberīy default, the stored procedure definition at the Publisher is propagated to each Subscriber. Replication Transact-SQL Programming: execute sp_addarticle (Transact-SQL) and specify a value of 'serializable proc exec' (recommended) or 'proc exec' for the parameter For more information about defining articles, see Define an Article. SQL Server Management Studio: Publish the Execution of a Stored Procedure in a Transactional Publication (SQL Server Management Studio) To publish the execution of a stored procedure Similarly, if an update is based on a subquery of another, nonreplicated table, executing the same stored procedure at both the Publisher and Subscriber returns different results. If an article is filtered horizontally, so that there are different sets of rows at the Publisher than at the Subscriber, executing the same stored procedure at both returns different results. Stored procedure replication is not appropriate for all applications. With the replication of stored procedure execution, replication sends only the command to execute the stored procedure at the Subscriber, rather than writing all the updates to the distribution database and then sending them over the network to the Subscriber: EXEC give_raise
UPDATE EMPLOYEES SET salary = salary * 1.10 WHERE PK = 'emp 2' UPDATE EMPLOYEES SET salary = salary * 1.10 WHERE PK = 'emp 1' Without the replication of stored procedure execution, the update would be sent to Subscribers as a large, multi-step transaction: BEGIN TRAN When you execute this stored procedure at the Publisher, it updates the salary for each employee. This procedure gives each of the 10,000 employees in your company a 10 percent pay increase. UPDATE EMPLOYEES SET salary = salary * 1.10 For example, assume you create the following stored procedure in the publication database: CREATE PROC give_raise AS This can provide significantly better performance for cases where large batch operations are performed, because only the procedure execution is replicated, bypassing the need to replicate the individual changes for each row. The definition of the procedure (the CREATE PROCEDURE statement) is replicated to the Subscriber when the subscription is initialized when the procedure is executed at the Publisher, replication executes the corresponding procedure at the Subscriber. If you have one or more stored procedures that execute at the Publisher and affect published tables, consider including those stored procedures in your publication as stored procedure execution articles. Applies to: SQL Server Azure SQL Managed Instance


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
